The Cart Abandonment Rate on a website is an essential key performance indicator (KPI) that reveals potential missed opportunities in an ecommerce business. By monitoring this metric, businesses can gain insight into the hurdles or challenges customers face during the checkout process.

This KPI, when analyzed correctly, offers a window into optimizing the customer journey, enhancing the buying experience, and subsequently boosting conversion rates.
Key Takeaways
- Definition: Cart Abandonment Rate (CAR) reveals the percentage of users who add products to their cart but do not complete the purchase.
- Calculation: CAR is determined by subtracting the ratio of Total Paid Orders to Total Add to Cart actions from one.
- Strategic Importance: Monitoring CAR helps businesses identify lost revenue opportunities and improve the user experience.
- Optimization Strategies: To reduce CAR, businesses can streamline the checkout process, offer transparent pricing, and leverage retargeting campaigns.
- Limitations of CAR: CAR does not account for mere browsing, varies by product, can be skewed by technical glitches, does not differentiate between user types, is influenced by external factors, does not necessarily mean permanent lost sales, can lead to misguided business decisions if overemphasized, and requires consistent monitoring to identify accurate trends.
- Complementary Metrics: CAR should be evaluated alongside metrics such as conversion rate, average order value, and site traffic for a complete understanding of user behavior.
Why does Cart Abandonment Rate on Website matter for your business?
Understanding and addressing a high Cart Abandonment Rate can lead to considerable benefits for an ecommerce enterprise:
- Lost Revenue Recognition: Identifying and rectifying the reasons behind cart abandonment can help recover potential revenue.
- Enhanced User Experience: Analyzing reasons for cart abandonment can guide improvements in the user journey, leading to a smoother and more efficient shopping experience.
- Optimized Checkout Process: Pinpointing challenges in the checkout process and rectifying them can reduce friction and increase conversions.
- Strategic Marketing: Armed with data on cart abandonment, businesses can launch targeted remarketing campaigns to woo back customers and incentivize completion of their purchases.
- Improved Product Descriptions: High abandonment might indicate that product information isn’t clear or comprehensive. Enhancing product details can instill better confidence in shoppers.
How to calculate Cart Abandonment Rate on Website (CAR)?
Explanation of the parts of the formula:
- Total Paid Orders from Website refers to the number of orders on the website that were finalized with a payment. Essentially, these are orders where the transaction was successful, and the customer made a payment.
- Total Add to Cart on Website signifies the cumulative number of instances when users added products to their shopping cart, regardless of whether they completed the purchase or abandoned it.
- The subtraction (1 – ratio) gives the proportion of users who added products to their cart but did not finalize the purchase. This value, when represented as a percentage, is the Cart Abandonment Rate.
- Multiplying by 100 in the formula simply converts the decimal value into a percentage, making it more intuitive and understandable.
In essence, the Cart Abandonment Rate is a metric used to determine the percentage of potential customers who initiate the buying process but don’t complete it. A higher rate may suggest challenges in the checkout process or other barriers preventing users from finalizing their purchase.
Example Scenario
Let’s visualize it with a hypothetical situation:
- Over a particular month, 1,200 items were added to carts on your website.
- Out of these 1,200 additions, 900 orders were paid and completed.
To calculate the Cart Abandonment Rate using the given formula:
- Cart Abandonment Rate (\%) = \(1 – 900/1,200) × 100
- Cart Abandonment Rate (\%) = (1 – 0.75) × 100
- Cart Abandonment Rate (\%) = 0.25 × 100
- Cart Abandonment Rate (\%) = 25%.
This implies that, during that month, 25% of users who added items to their cart did not proceed to complete their purchase.
Cart Abandonment Rate on Website (CAR) benchmarks
Globally, the average shopping cart abandonment rate is 71.42%.
In July 2023, Beauty & Personal Care topped the list with the highest cart abandonment rate of 82.87%, a slight increase of 0.35% from June. Over the past year, Beauty & Personal Care has consistently seen the highest cart abandonment rates, averaging 82.26%. In contrast, Consumer Products had the lowest drop-off rate, averaging 36.08%.
Regionally, APAC topped the chart with the highest overall cart abandonment rate at 78.89%. It was closely followed by EMEA at 75.04% and the Americas at 70.63%.
Broken down by device type, mobile users accounted for the majority of cart abandonment, with 77.35%. Tablet users were next with a rate of 64.4%, while desktop users accounted for 60.04%.
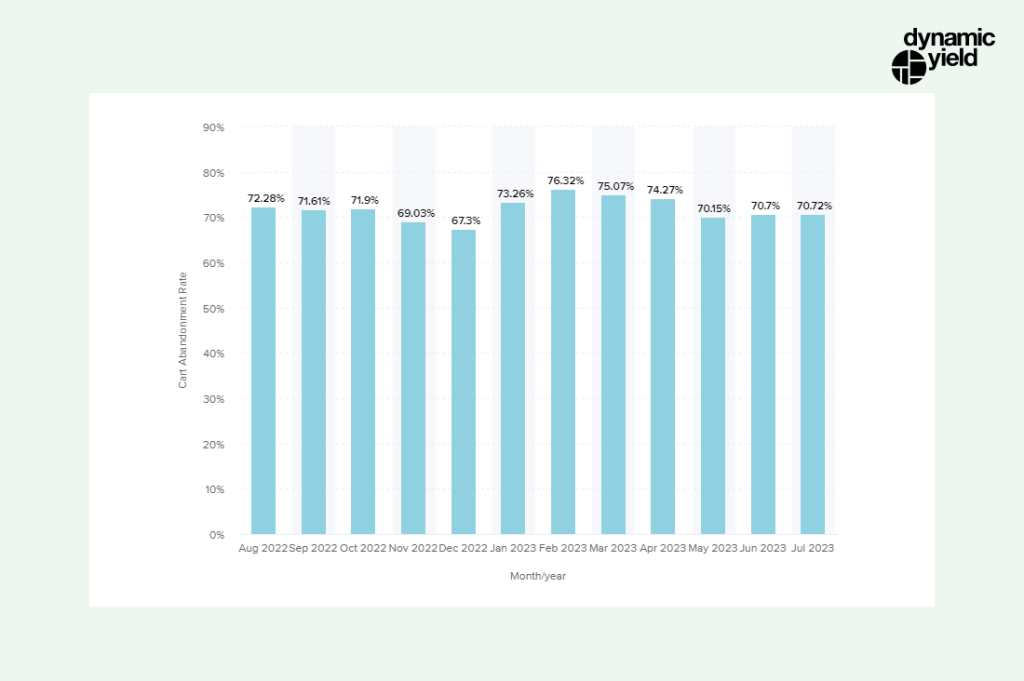
The average shopping cart abandonment rate globally is 71.42%. MoM cart abandonment rate breakdown - % of items left in carts and not purchased by visitors over the past twelve months.
Tips and recommendations for reducing Cart Abandonment Rate on Website
Streamlined the Checkout Process
The checkout process is the last hurdle before a customer completes a purchase. It’s important to simplify this process so that customers are not deterred by unnecessary steps or complications. Ideally, your checkout should be a concise, linear process that takes the customer from shopping cart to confirmation as smoothly as possible.
- Reduce the number of steps: Limit the checkout process to what’s necessary. Too many steps can make the process seem tedious and lead to cart abandonment.
Offer guest checkout options: Not everyone wants to create an account just to make a purchase. Offering a guest checkout option can increase conversions by reducing friction. - Make the process intuitive: The process needs to be straightforward and easy to follow. Avoid industry jargon and use clear, concise language.
Transparent pricing and fees
Unexpected costs are one of the top reasons for shopping cart abandonment. Being upfront about all fees can significantly reduce this.
- Display all additional fees: This includes shipping, handling, or any other additional costs. Make these clear early in the process to avoid unpleasant surprises at checkout.
- Display taxes up front: Taxes can add significantly to the final price. It’s best to include them in the product price, or at least mention the applicable rates on the product page itself.
Multiple payment options
Customers appreciate having a choice when it comes to payment methods.
- Offer popular payment options: This includes credit/debit cards, net banking, PayPal, and other popular payment methods.
- Offer localized payment methods: Depending on your market, consider including local payment methods or digital wallets that are popular in the region.
Trust Signals
Trust signals help assure customers that their transaction is secure and your business is trustworthy.
- Security badges: Display SSL certificates or security badges from respected institutions to show that your site is secure.
- Customer reviews and testimonials: Provide social proof that other customers have had positive experiences with your products or services.
Easy navigation and user interface
A well-designed website is essential for a smooth shopping experience.
- User-friendly design: The site should be easy to navigate, with products logically categorized and a search function for easy access.
- Mobile responsive: With more and more customers shopping on their phones, your site needs to be mobile-friendly.
- Error-free: Regularly check your site for any glitches or performance issues that could disrupt the shopping experience.
Retargeting Strategies
Retargeting strategies can help remind customers of items they’ve left in their shopping carts and encourage them to complete their purchases.
- Retargeting ads: These ads can remind customers of their abandoned carts as they browse other websites or social media platforms.
- Email campaigns: A well-timed email reminder about an abandoned cart, perhaps offering a small discount or incentive, may be just what’s needed to get the customer to complete their purchase.
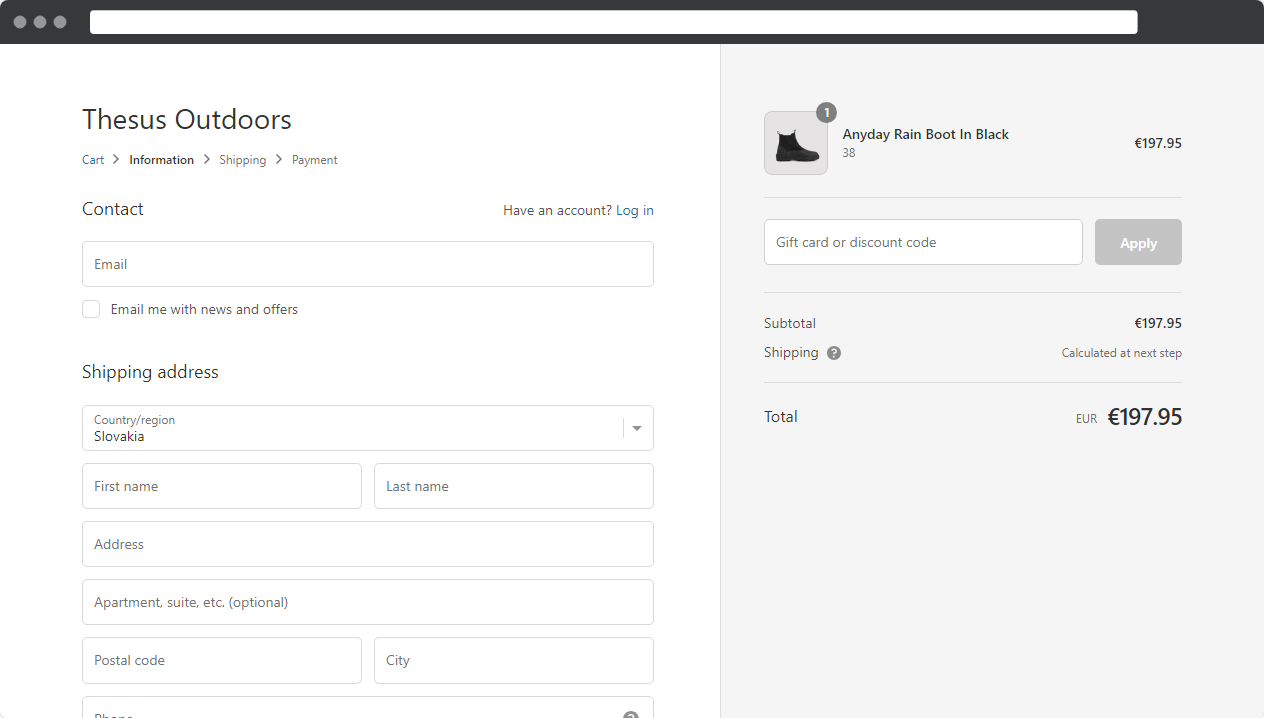
A simple and clear checkout reduces cart abandonment. Such a checkout is typical for e-commerce built on the Shopify platform.
Examples of use
Intuitive Checkout Design
- Scenario: An online electronics store notices a spike in cart abandonment after redesigning their website.
- Use Case Application: A potential solution could involve revisiting the new design, focusing on the checkout process. By introducing a more intuitive layout, reducing the number of required fields, and adding a progress bar, the store can provide clarity and convenience, likely reducing the abandonment rate.
Retargeting Campaigns
- Scenario: A fashion ecommerce site detects a high abandonment rate despite users spending a significant time browsing products.
- Use Case Application: Recognizing the potential intent to buy, the brand can deploy retargeting ads showcasing the abandoned products, coupled with time-limited discount codes. This re-engages potential buyers, nudging them towards purchase completion.
Personalized Recommendations
- Scenario: An online grocery store observes that users frequently abandon carts that contain only one or two items.
- Use Case Application: In order to encourage users to proceed to checkout, the store can integrate a system that suggests personalized product recommendations based on what’s already in the cart. For instance, if a user has only added spaghetti, a prompt could suggest tomato sauce or cheese. This not only potentially increases the cart value but also encourages the user to complete the purchase.
Transparent Pricing
- Scenario: A travel booking platform receives feedback that users are abandoning their carts due to unexpected fees showing up at the final payment step.
- Use Case Application: The platform can ensure pricing transparency throughout the booking process. All potential fees, taxes, and surcharges should be made clear from the outset or, at the very least, before the user reaches the final payment step. By reducing unexpected costs, users will be more likely to trust the platform and finalize their booking.
Live Chat Support
- Scenario: A home appliances e-commerce site finds that users often abandon carts after spending a long time on product specification pages.
- Use Case Application: Recognizing that users may have unresolved questions leading to indecision, the site can introduce a live chat feature. This provides users with real-time assistance, clarifying product specifications or addressing concerns they might have, making them more confident in completing the purchase.
Example of using trust signals badges on a product detail. Several themes allow to display the badge block via hooks. This example is from the Shoptimizer theme for Woocommerce.
Cart Abandonment Rate on Website SMART goal example
Specific – Decrease the cart abandonment rate on the website by 10% (from the current rate of 60% to 50%).
Measurable – The cart abandonment rate will be monitored and compared weekly using the eCommerce analytics platform before and after implementing website and checkout process optimizations.
Achievable – Yes, by enhancing the checkout user experience, offering guest checkout options, introducing retargeting campaigns, sending abandoned cart reminder emails, and optimizing page load times.
Relevant – Yes. Reducing the cart abandonment rate is crucial for increasing sales without necessarily driving more traffic to the website. This objective aligns with the monthly goal of boosting conversions and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Timed – Within five months of implementing the recommended changes and optimizations.
Limitations of using Cart Abandonment Rate on Website
Cart Abandonment Rate (CAR) is a key metric in ecommerce for understanding how many shoppers start the purchase process but don’t complete it. However, it has its own limitations:
- Doesn’t Account for Browsing Behavior: Many users add items to their cart as a part of their browsing or research process without the intent to buy immediately. They may be comparing prices, saving for later, or simply window shopping. CAR doesn’t distinguish between these behaviors.
- Varies Across Product Types: Some products naturally have higher abandonment rates due to the nature of the purchase decision. For instance, expensive luxury items may have a higher CAR than everyday consumables. Comparing CAR across diverse product categories can be misleading.
- Can Be Influenced by Technical Issues: High CAR might not always reflect a problem with the product or price. Technical glitches, website downtime, or a complicated checkout process can lead to increased abandonment.
- Doesn’t Differentiate Between Guest and Registered Users: Registered users might have a different CAR than guest users. They may add items to the cart to take advantage of wish-list type features and buy later, which can inflate the CAR.
- Doesn’t Consider External Factors: Factors like increased competition, economic downturns, or seasonal shopping behaviors can impact CAR. It’s essential to consider the broader context when analyzing this metric.
- Does Not Always Indicate Lost Sales: Just because a cart is abandoned doesn’t mean the sale is lost forever. Users may return later to complete the purchase, especially if retargeting strategies are used.
- Overemphasis Can Lead to Inaccurate Conclusions: Solely focusing on reducing CAR might lead businesses to offer too many discounts or make unnecessary changes to their website, affecting profitability.
- Requires Regular Monitoring: CAR can fluctuate over short periods, depending on promotions, stock availability, and other factors. It’s vital to monitor it regularly to ensure accuracy and to identify trends over time.
In summary, while Cart Abandonment Rate provides critical insight into the shopper journey, it’s only one piece of the puzzle. Relying on CAR alone to make decisions can lead to misinterpretations and missed opportunities. It’s critical to combine it with other metrics to gain a holistic understanding of the ecommerce landscape.
KPIs and metrics relevant to Cart Abandonment Rate on Website
-
Conversion Rate: An inverse relationship generally exists between conversion rate and cart abandonment rate. A low conversion rate alongside a high cart abandonment rate may signal friction in the checkout process.
-
Average Order Value (AOV): If customers frequently abandon high-value carts, it may indicate sticker shock or concerns about product authenticity.
- Site Traffic: Monitoring site traffic in conjunction with cart abandonment can provide insights into user behavior and website performance.
- Customer Feedback: Gathering direct feedback can offer specific reasons behind cart abandonment, providing actionable insights.
By understanding and addressing the Cart Abandonment Rate in tandem with these metrics, your business can make more informed decisions to enhance user experience and sales.
Final thoughts
The Cart Abandonment Rate serves as a critical indicator of potential revenue leakage and user experience challenges in an e-commerce environment. Addressing the underlying reasons for cart abandonment can lead to significant increases in revenue, improved user experience, and greater customer loyalty. A proactive approach to this metric is essential for any ecommerce business seeking sustainable growth.
Useful links
Cart Abandonment Rate on Website (CAR) FAQ
What is Cart Abandonment Rate?
It denotes the percentage of users who added items to their online shopping cart but exited without completing the purchase.
Why is addressing Cart Abandonment Rate vital?
Reducing cart abandonment directly influences revenue recovery, improved user experience, and better conversion rates.
How can businesses decrease Cart Abandonment Rate?
Strategies encompass improving the checkout process, being transparent about prices and fees, and deploying targeted retargeting campaigns.
Does a high Cart Abandonment Rate always signal a problem?
While often it does, occasional spikes might result from external factors like website downtime or broader economic conditions. Continuous monitoring and analysis are essential.
Can external factors influence Cart Abandonment Rate?
Absolutely. Website performance, broader market conditions, competitor pricing, and global events can all impact cart abandonment rates.